Join / Login Question Which of the following is produced when R R − O H P C l 5 → A BGet answer Complete the following (i) ROH PCl_(5) rarr (ii) ROHPCl_(3) rarr Roh pcl5 mechanism Roh pcl5 mechanismPreparation of Alkyl Bromides Unlike PCl 3, the compounds PBr 3 and PI 3 are not stable and hence they are to be prepared when they are to be used by treating bromine and iodine with red phosphorous Compounds PBr 5 and PI 5 do not exist Alkyl bromides are prepared by the action of bromine, in
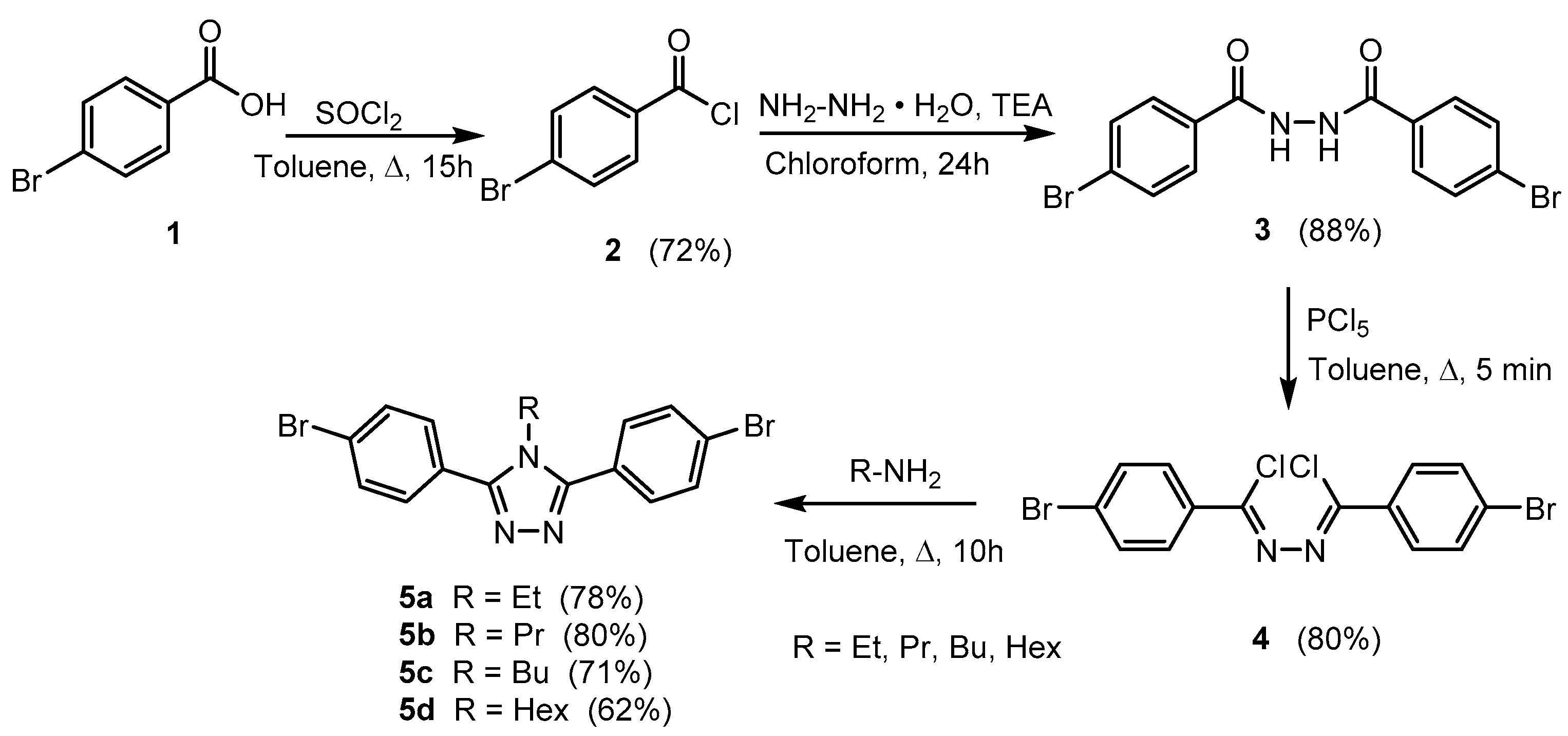
Materials Free Full Text Highly Luminescent 4h 1 2 4 Triazole Derivatives Synthesis Molecular Structure And Photophysical Properties Html
R-oh + pcl5
R-oh + pcl5- Reaksi dengan PCl 5 Eter/alkoksialkana dapat bereaksi dengan PCl 5 membentuk kloroalkana dan POCl 3 R – O – R' PCl 5 –> R – Cl R' – Cl POCl 3 Reaksi dengan asam halida Jika asam halida HX terbatas maka R – O – R' HX –> R – OH R' – X (R lebih panjal dari R') Jika asam halida HX berlebih makaWatch Video in App Continue on Whatsapp



Chemical Forums Mechanism Of Substitution Of Oh Group With Cl Using Pcl5
Alcohols can be prepared by hydration of Alkenes , Hydrolysis of Alkyl halides , Oxidation of Ketones / Aldehydes , From Grignard's Reagent , Hydroboration Oxidation Alcohols undergo Oxidation , Esterification , Reactions with Metals , HCl , HBr , HI , PCl3 , PCl5 , SOCl2 Phenol is Carbolic Acid Phenols are prepared by Dow Process , Raschig Process , Diazotization and fromR'OH cat H2SO4 SOCl2 PCl3 (COCl)2 PBr3 P2O5, heating H2NR DCC H2O, H heating Title handoutacid03PDF Author chang Created Date 2/24/03 AMClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Which of the following is the byproduct when R OH is reacted with PCl3 ?Instructions To balance a chemical equation, enter an equation of a chemical reaction and press the BalanceIn each case a base is used to "mopup" the acidic byproduct
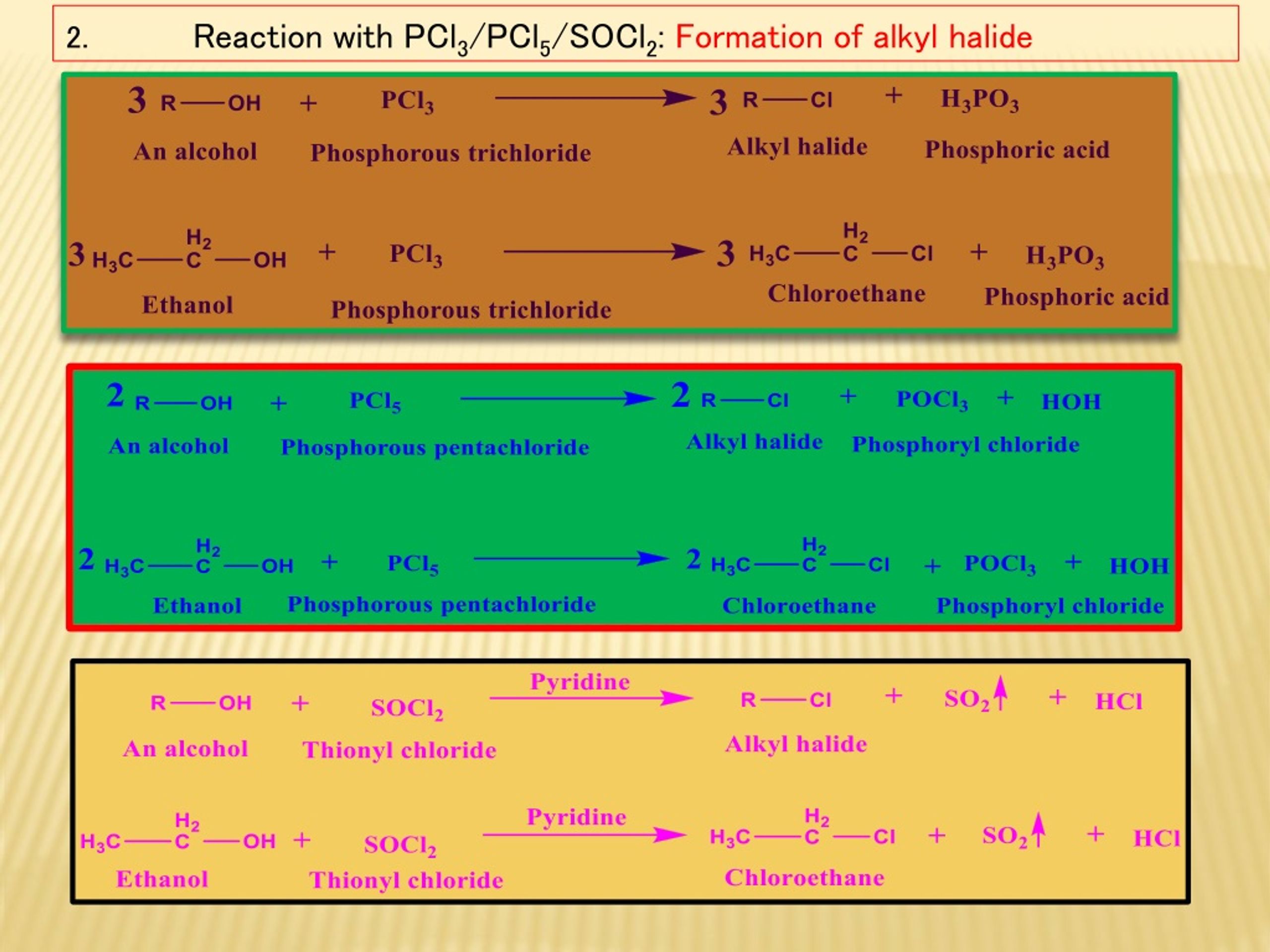
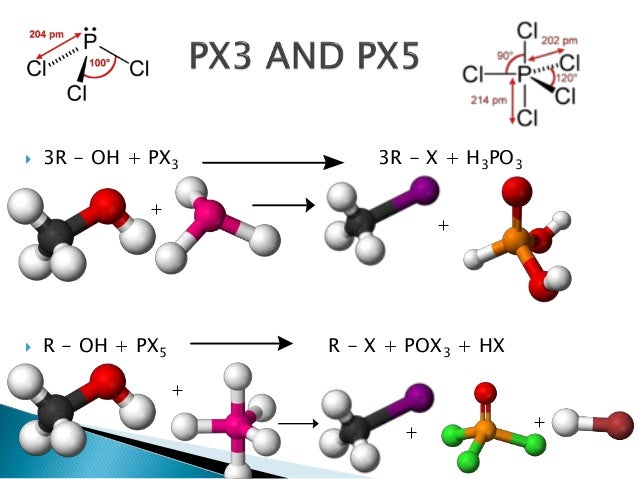
3 ROH PCl 3 3 RCl P(OH) 3 3 ROH PBr 3 3 RBr P(OH) 3 ROH PCl 5 RCl POCl 3 HCl PI 3 has to be generated in situ via reaction of iodine and phosphorous Eg CH 3 (CH 2) 14 CH 2OH P/I 2 CH 3 (CH 2) 14 CH 2I This type of reaction does not work well for tertiary alcohols, and also does not lead to rearranged productsAnswer (1 of 3) I'm putting the answer forward See mechanisms in Chemistry are to explain the phenomenas observed experimentally and hence, at times, you might feel that some steps are forceful but they are at place for explaining experimental results and carrying the Actually, while it s true that PCl5 is commonly used to convert the OH group of an alcohol or carboxylic acid to Cl, it also undergoes a reaction with aldehydes and ketones at low temperature (usually use 0 degrees C when writing it on paper), converting RCOR to RCCl2R (ketone to geminal dichloroalkane) and RCHO to RCHCl2 (aldehyde to geminal dichloroalkane)
Reaction OF RX with KNo2 ,AgNo2, KCN, AgCN Reaction OF PCl5 with ROH , RCOOH etc Updated On 7421 To keep watching this video solution for FREE, Download our App Join the 2 Crores Student community now! Organic Chemistry Alcohol 1 50 Alcohol ~ Organic compound with at least one hydroxyl group (–OH) which act as functioning group Alcohol has the general formula of CnH2n1OH or sometimes CnH2n2O The naming of alcohol end with ~ol 51 Nomenclature of alcohol (naming & classifying alcohol) The way of naming alcohol is similar to the wayR OH > R OHReaction with HX This reaction takes place in presence of zinc chloride and the equation involved is given below Reaction With PCl 5 and PCl 3;




Balance Pcl5 H2o Pocl3 Hcl By Hit And Trail Method Brainly In




How Does Ethyl Alcohol React With Pcl5
128 UTTAM'S XII Chemistry Papers Solution CHART Reactions of Carboxylic Acid NaHCO3/Na/NaOH/Na2CO3 R COONa Acidic properties SOCl2 or PCl3 O Acyl chloride or PCl5 R C Cl R OH O P2O5, R C O R Ester OO R C O C R Anhydride R COOH NH3 O Amide Carboxylic R C NH2 Acid LiAlH4/ether R CH2OH Alcohol H3O R H Alkane Na, NaOH, CaO X2/red phosphorus R CHR C O H2O 2 R'OH 2 NHR'R'' 2RC O OH 2 R C O OR' R C O NR'R" 2 Reactions are even slower with esters R C O OR' H2O, heat HNR'R" R C O OH R C O NR'R" Amides are unreactive and need strong acid or base to hydrolyze them to acids All of the reactions shown proceed by the same general mechanism eg hydrolysis of acyl halide RC O Cl HOH RC OClModify Create Phosphorus pentachloride is a greenishyellow crystalline solid with an irritating odor It is decomposed by water to form hydrochloric and phosphoric acid and heat This heat may be sufficient to ignite surrounding combustible material It is corrosive to metals and tissue




Socl2 Reaction With Carboxylic Acids Chemistry Steps




Alcohols Friday 16 November Ppt Download
R–OH X• Alcohols (ROH) Reaction with phosphorus pentachloride Add a spatula measure of PCl 5 solid to 1 cm 3 of the liquid to be tested An exothermic reaction which evolves steamy fumes (HCl) which turn damp litmus red and form a white 'smoke' with ammonia gas confirms the presence of an –OH group in the moleculeUsed mostly for 1 o and 2 o ROH (via S N 2 mechanism);Complete the following reaction ROH PCl5 →\rightarrow→ RCl X HCl X is PCl3, PCl5, POCl3, POBr3




Doubt From Aldehydes And Ketones Organic Chemistry Doubts Goiit Com




Complete The Following I R Oh Pcl 5 Rarr Ii R Oh Pcl 3 Rarr
The reaction of alcohols R O H with P C l X 5 and P C l X 3 yields an alkyl halide R C l With P C l X 5, the reaction is quite simple leading to the formation of R C l and P O C l X 3 But with P C l X 3 a problem arises Since P C l X 3 has both a lone pair and vacant 3 d orbitals it can act both as a Lewis base and a Lewis acidR Oh Pcl5 Gives To Roh pcl5 Roh pcl5Connect with Facebook Connect with Google or connect using your email or mobile OR Email or Mobile Password Target Year 17 18 19 embibers login here to continueClick here👆to get an answer to yourRoh pcl5 Roh pcl5 ROH PCl5 => RCl POCl3 HCl Bromination Reagent Potassium bromide (KBr) in a 50% concentrated sulfuric acid solution (as an acid catalyst) The potassium bromide and the sulfuric acid will react to produce hydrogen bromideROH RCOOH → RCOOR H 2 O CH 3 OH CH 3COOH → CH 3COOCH 3 H 2 O Note A sweet smell indicates the



1




L 15 R Cooh Reaction With Socl2 Pcl5 Pcl3 With Mechanism Jee Neet Youtube
PCl 5 4H 2 O → H 3 PO 4 5 HCl Phosphorus pentachloride reacts with sulfur dioxide forms Phosphoryl chloride and Thionyl chloride SO 2 PCl 5 → POCl 3 SOCl 2 Uses of Phosphorus Pentachloride – PCl 5 Used as a chlorinating agent and catalyst ш making organic chemicals, intermediates, dyestuffs, etc Reaksi dengan asam halida (HX) Eter dapat bereaksi dengan asamhalida (terutama HI) menghasilkan alkil halida dan alkohol R – O – R' HI → R – OH R' – I Jika asam halidanya berlebih, akan dihasilkan 2 molekul alkil halida Contoh What is the mechanism of 3(ROH PCl3) Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Solutions;




Materials Free Full Text Highly Luminescent 4h 1 2 4 Triazole Derivatives Synthesis Molecular Structure And Photophysical Properties Html




R Oh Pcl5 Gives To
Reaction of carboxylic acid with alcohol, pcl3,pcl5,socl2,NH3Alkyl bromides can be prepared in a similar reaction using PBr 3;ROH PCl 5 > RCl POCl 3 H 2 O Alcohol PhosphorousPentachloride ChloroAlkane PhosphorylChoride




Substrate Specificity Of Cytolase Pcl5 For Platycosides Download Scientific Diagram



Practice Questions Alcohols And Phenols
3 ROH PCl 3 3 RCl H 3 PO 3 Alcohol phosphorous trihalide alkyl halide phosphorous acid Example – 1 Preparation of ethyl chloride (Chloroethane) from ethyl alcohol (Ethanol) 3C 2 H 5 OH PCl 3 3C 2 H 5 Cl H 3 PO 3Sedangkan eter tidak melepas gas HCl melainkan membentuk dua alkil clorida Alkohol R – OH PCl 5 –> R – Cl POCl 3 HCl Eter R – O – R' PCl 5 –> R – Cl R' – Cl POCl 3 Solution Alkyl alcohol is mixed with phosphorous trichloride and alkyl chloride is formed along with Pyridine in the above reaction 14k 278k Complete the following (i) (ii)




Ch 8 Roh Socl2 Or Px3




Alcohol Or Carbonyl Which Is More Reactive Towards Pcl5 Chemistry Stack Exchange
) between C and O, RC*OH 1 Reaction with PCl5, PCl3, SOCl2 and HX 2 Lucas test and its observations (turns cloudy) Reaction of 1°, 2°, 3° ROH with ZnCl2 conc HCl 3 Dehydration reaction (2 types) Reaction with hot concentrated sulphuric acids a primary alcohol (1° ROH) with one alpha hydrogenAnswer (1 of 2) The Oxygen of the "OH" group in phenol is strongly bound to the benzene ring hence it cannot be easily replaced Though phenol react w/t PCl5 to give chloro benzene, other reagents like HCl, POCl3 C6H5OH PCl5 —› C6H5ClR OH O R Cl O 1 SOCl 2 2 R'OH R OR' O • mechanism required for acid chloride to ester conversion additioneliminationdeprotonation • Conversion of the acid chloride to the ester is a "downhill" reaction energetically 14 Direct Conversion to Amides (Sections 11, 13, 215) R OH O RNH2, heat R NHR O • mechanism not required




Poly ϵ Caprolactone Functionalized Carbon Nanofibers By Surface Initiated Ring Opening Polymerization Wang 07 Journal Of Applied Polymer Science Wiley Online Library
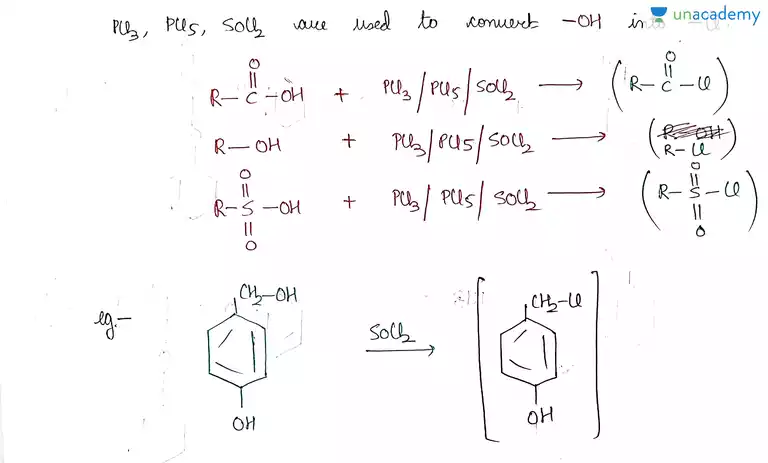



Iit Jee Reaction With Pcl5 Pcl3 Socl2 And Hx Offered By Unacademy
OH HO O (S)() Malic acid aD= 23 ° PCl5 OCl OH HO O Ag2O, H2O OOH OH HO O (R)() Malic acid aD= 23 ° PCl5 Ag2O, H2O OCl OH HO O ()2Chlorosuccinic acid ()2Chlorosuccinic acid The displacement of a leaving group in a nucleophilic substitution reaction has a defined stereochemistry Stereochemistry of nucleophilic substitutionCreate Phosphorus oxychloride appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor Density 140 lb / gal Very toxic by inhalation and corrosive to metals and tissue Used in gasoline additives and hydraulic fluids CAMEO Chemicals Phosphoryl trichloride is a phosphorus coordination entityPCl5 3 (COCl)2 Anhydrides R O O R O R OH O 2 P 2 O 5 Activating Agents Carbonyl Diimidazole R OH O N N O N N R N O N N NH CO Acyl Imidazole PROTECTING GROUPS 63 Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide N C N R OH O R O O C N C 6 H 11 C 6 H 11 R NH Nu O C 6 H 11 N H N H C 6 H 11 O Nu Ketene formation is a common side reaction scambling of chiral



Chemical Forums Mechanism Of Substitution Of Oh Group With Cl Using Pcl5
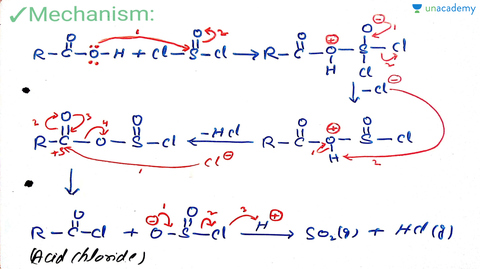



Neet Ug Reaction With Pcl5 Pcl3 And Socl2 And Reaction With Ammonia Offered By Unacademy
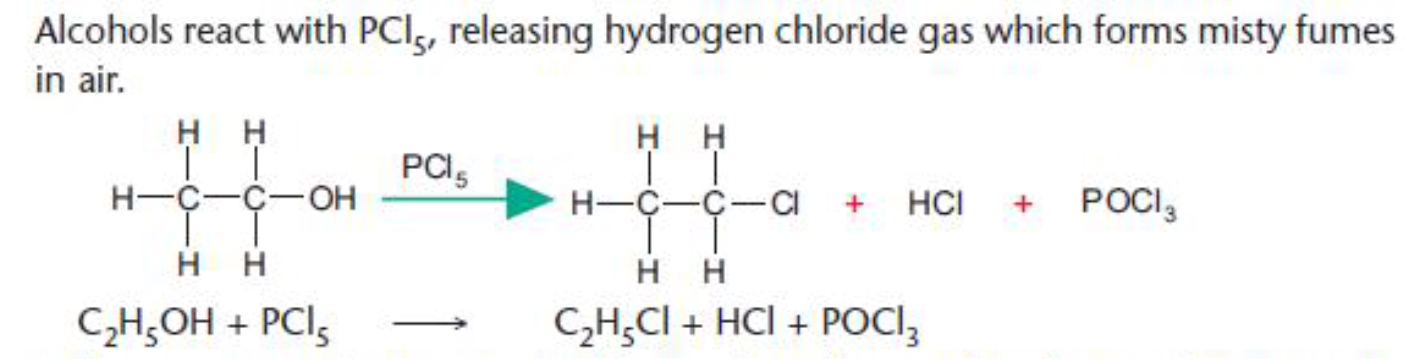
3 ROH PCl 3 3 RCl P(OH) 3 3 ROH PBr 3 3 RBr P(OH) 3 ROH PCl 5 RCl POCl 3 HCl PI 3 has to be generated in situ via reaction of iodine and phosphorous Eg CH 3 (CH 2) 14 CH 2OH P/I 2 CH 3 (CH 2) 14 CH 2I This type of reaction does not work well for tertiary alcohols, and also does not lead to rearranged productsReagentPlus ®, 99% Synonym Phosphorus (III) chloride CAS Number LinearPREPARATION OF ALKYL HALIDES Mono haloalkanes or Alkyl halides can be prepared by a number of methodsSome important synthetic methods are as follows METHOD No 1 BY USING ALCOHOL AS A MAIN REAGENT A number of reagents such as halogen acids, PCl 5, PCl 3, SOCl 2 etc react with aliphatic alcohols to produce corresponding alkyl halidesClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ R OH PCl5→ A B C Identify A,B & C




Which Of The Following Is The Byproduct When R Oh Is Reacted With Pcl3
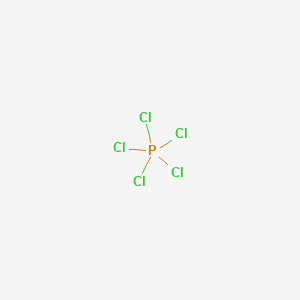



Phosphorus Pentachloride Pcl5 Pubchem
Platycosides are the functional saponins present in balloon flowers that exert diverse biological effects, and which can be further improved by their deglycosylation Deapiosexylosylated platycodin D, which is absent in balloon flowers, can be generated only by cytolase PCL5 by acting on platycoside E To improve cytolase PCL5catalyzed production of deapiose Reaksi dengan PCl 5 Alkohol bereaksi dengan PCl 5 membebaskan gas HCl; Roh pcl5 Roh pcl5Reaction with phosphorus(V) chloride, PCl 5 Solid phosphorus(V) chloride (phosphorus pentachloride) reacts violently with alcohols at room temperature, producing clouds of hydrogen chloride gas It isn't a good choice as a way of making chloroalkanes, although it is used as a test for OH groups in organic chemistry$$\ce




File Action Of Phosphorus Pentachloride On Carboxylic Acid Png Wikipedia




Gautam Sir Chemistry Facebook
Reaction type Nucleophilic Substitution (S N 1 or S N 2) Summary Alcohols can also be converted to alkyl chlorides using thionyl chloride, SOCl 2, or phosphorous trichloride, PCl 3;Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Which of the following is produced when R OH react with PCl3 ?The greatest difference between the various oxidation states of bromine is 5 On acidification, the final mixture give bromin 5NaBrO 3 NaBrO 3 6HCl 6NaCl 3Br 2 3H 2 O Thus, during the reaction, bromine is present in four different oxidation states ie, zero in Br 2, 1 in NaBrO, 1 in NaBr and 5 in NaBrO 3




Compound A When Reacted With Pcl5 And Then With Ammonia Gave B B When Treated With Bromine And Caustic Potash Produced C C On Treatment With Hcl And Nano2 At 0 C



What Will Happen When C2h5no2 Reacts With Pcl5 Quora
R — OH PCl5 ¾¾¾® R — Cl POCl3 HCl Alcohol phosphoryl alkyl chloride chloride C2H5OH PCl5 ¾¾¾® C2H5 — Cl POCl3 HCl Ethyl alcohol ethyl chloride With PCl3 Alcohols react with PCl3 to form the corresponding alkyl chlorides, and phosphorus acidComplete the following (i) ROH PCl_(5) rarr (ii) ROHPCl_(3) rarrClass12Subject CHEMISTRYChapter ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLSBookDINESH PUBLICATIONBoardNE



What Happens When Benzoic Acid Reacts With Pcl5 Quora




Easy Trick Pcl5 Organic Reactions Jee Advanced Mains Neet By Arvind Arora Youtube




Bhartiyambhartiya Bhartiya With Your Class Section Rollno And Name Pcl5 H2o Acirc Dagger Rsquo H3po4




Reaction Of Alcohols With Pcl5 And Pcl3 Chemistry Stack Exchange
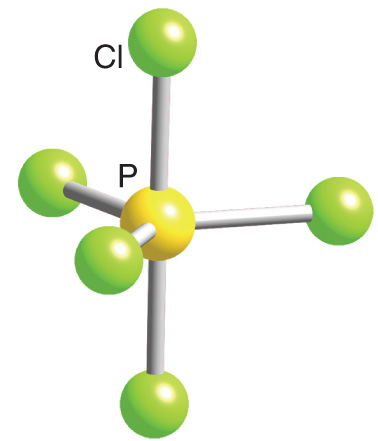



Phosphorus Pentachloride Pcl5




The Compound B Formed In The Following Sequence Of Reactions Ch3ch2ch2oh Pcl5 A Alc Koh B Is




Phenol Reacts With Pcl5 To Give Mainly Tardigrade In



Phenols React With Pcl5 The Student Room




Rcooh On Treatment With Pcl5 And Kcn Is Subjected To Hydrol
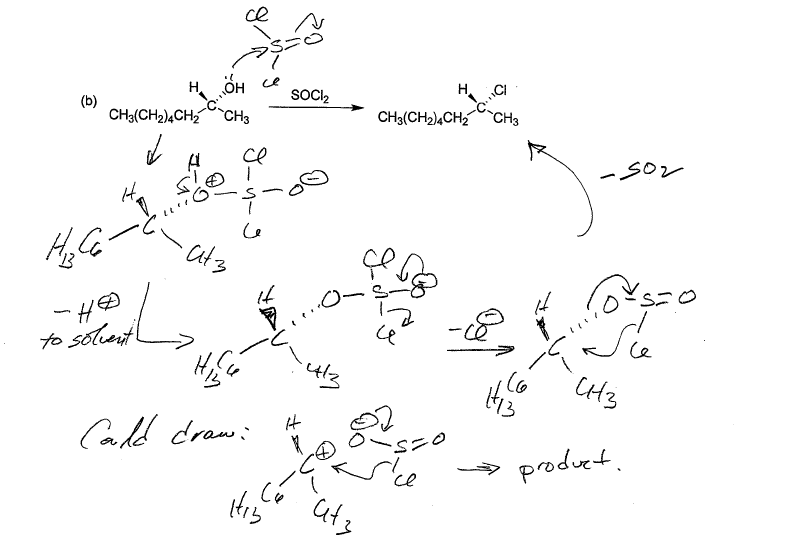



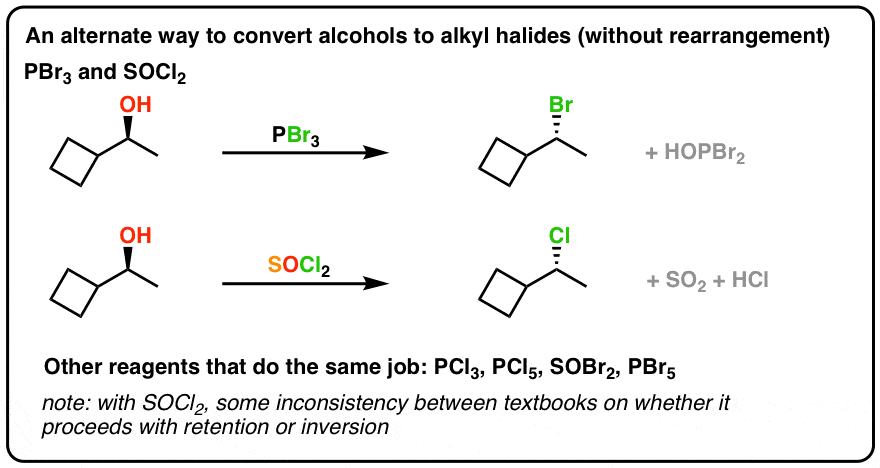
Socl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides Sn2 Versus Sni



What Is The Mechanism For A Reaction Between Alcohol And Phosphorus Pentachloride Quora



The Compound A On Treatment With Na Gives B And With Pcl5 Gives C B And C React Together To Give Diethyl Ether Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




File Beckmann Rearrangement Mechanism Nitrile Svg Wikimedia Commons




Ch3 Ch2 Ch2 Oh Use Pcl5 Brainly In
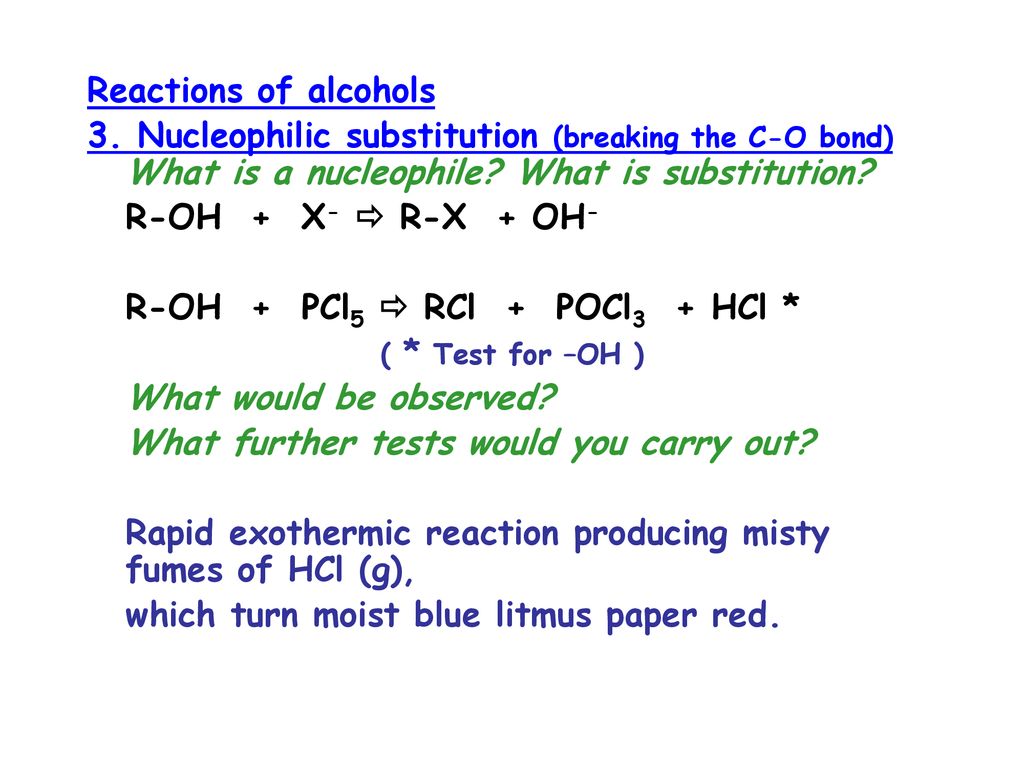



2 10 Reactions Of Alcohols Connector Ppt Download
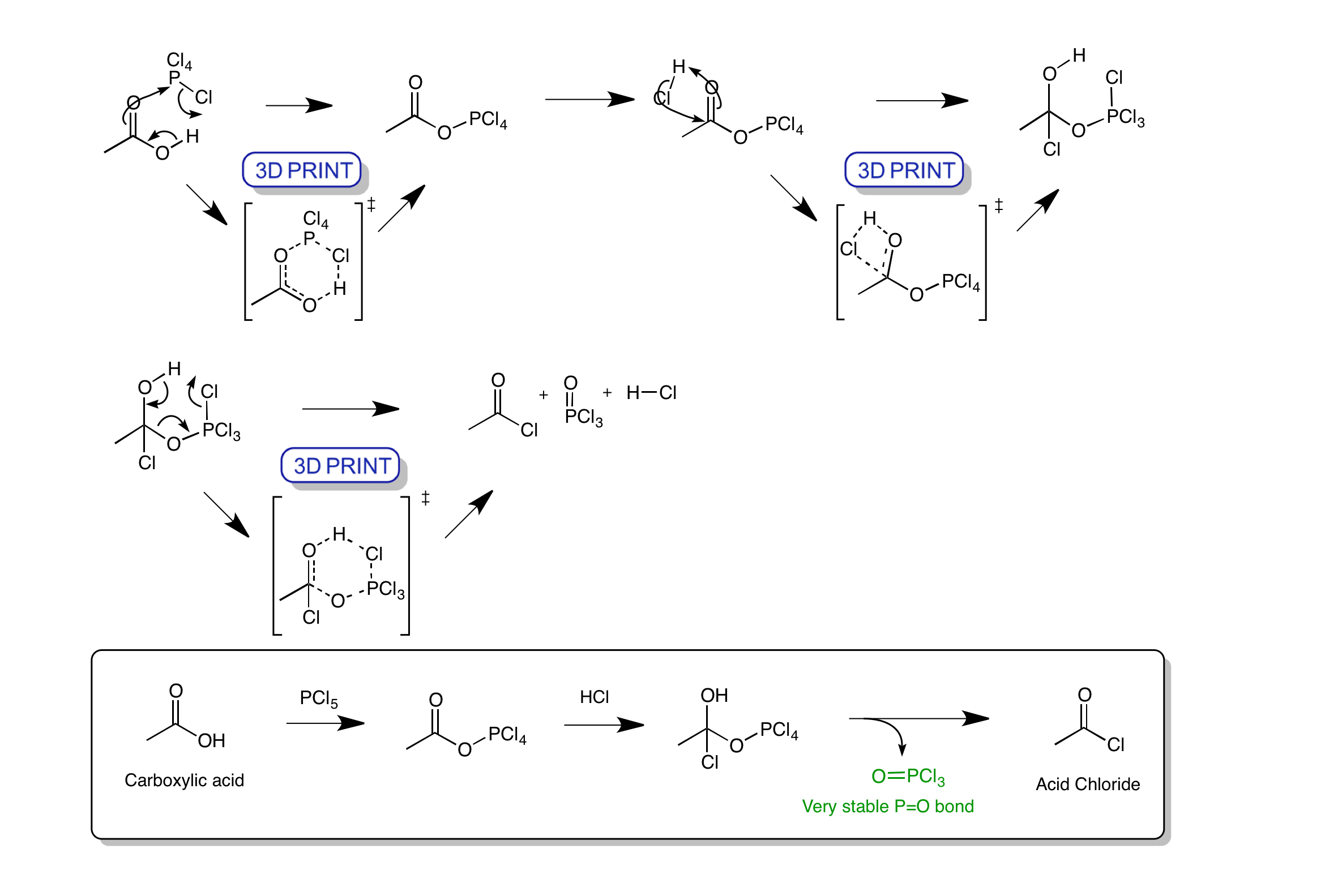



Acid Chloride Formation Phosphorus Pentachloride



What Is The Mechanism For A Reaction Between Alcohol And Phosphorus Pentachloride Quora




Q5 Select The By Product Formed In The Reaction Roh Pclg Here A Is Rci A A Pocl2 Hci B H3po3 No Other By Product C H3po3 Hci
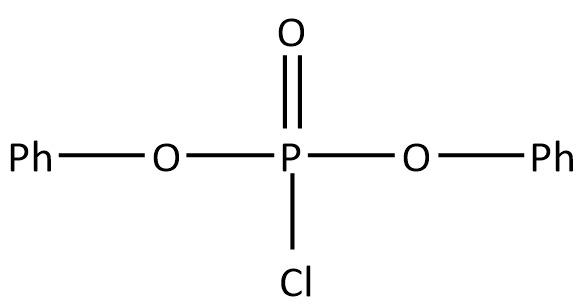



Phenol Reacts With Pcl5 The Main Product Is A B C D Class 11 Chemistry Cbse




Solved Phosphorus Pentachloride Pc15 An Important Reagent Chegg Com




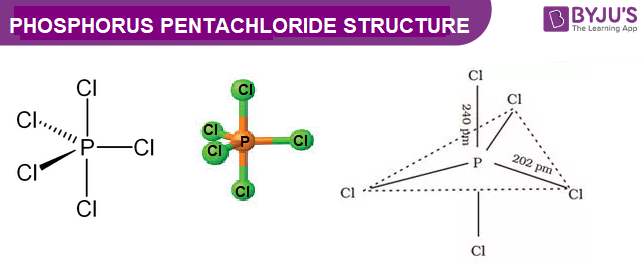
Phosphorus Pentachloride Wikipedia
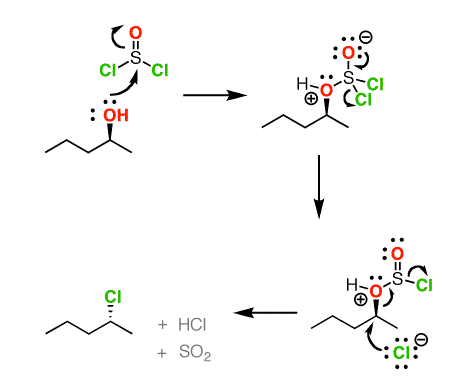



Socl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides Sn2 Versus Sni
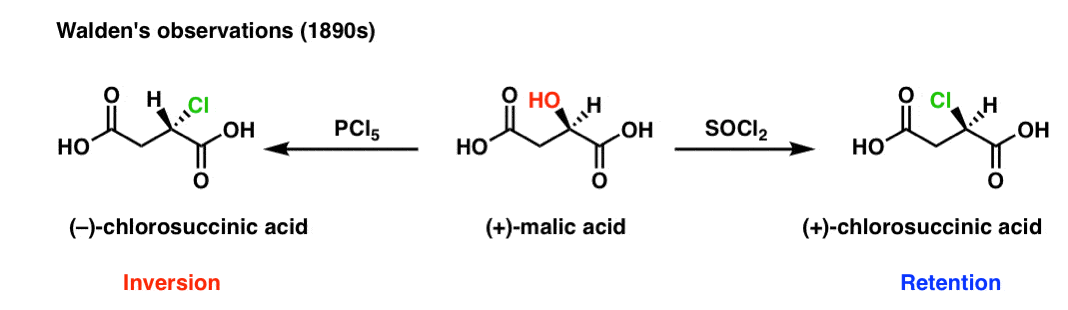



Socl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides Sn2 Versus Sni
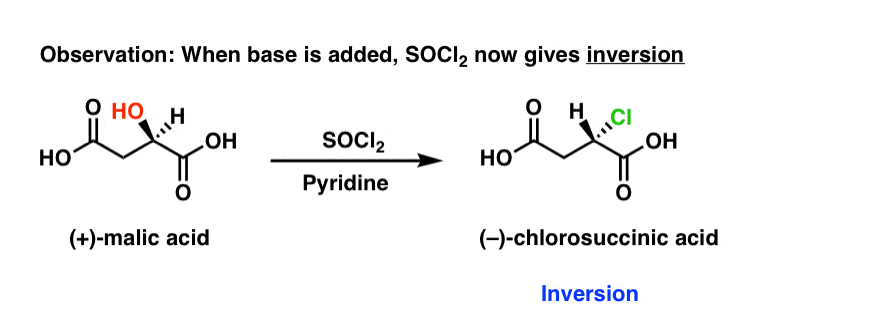



Socl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides Sn2 Versus Sni




18 Complete The Following Reaction A 3roh Pc13 B Roh Pcl5 Brainly In




Epb1 Procede Pour La Preparation De Tamsulosine Et Ses Derives Google Patents




Phosphorus Pentachloride Wikipedia



What Is The Major Product Of The Reaction Between Phenol And Pcl5 Quora



1



Ppt Alcohols Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 432




Pf5 And Pcl5 Interacting With Water Comparative Study At The Molecular Level Sciencedirect



Cdn S3waas Gov In




Revisitation Of The Pcl5 Chlorination Reaction Of A Amino Acids Spectroscopic And Dft Insights And Synthesis Of The L Proline Derived 2 5 Diketopiperazine Sciencedirect




Iit Jee Hydrolysis Of Ether And Reaction With Pcl5 Offered By Unacademy




Level 1 Questions Out Of Pcl5 And Socl2 Which One Is Halide Alkyl Halide And Water Water Forces Pdf Document



Pcl5 Phosphorus Pentachloride Structure Molecular Mass Properties And Uses



1



Phenol Reacts With Pcl5 The Main Product Is A B C D Class 11 Chemistry Cbse




Alcohols Advanced 6 Reaction Of Ethanol With Pcl5 Youtube




R Oh Pcl5 Gives To




R Oh Chrial Central And Is Optically Active It Is Subjected To Following Reaction I Roh Overset Pcl 5 To Overset Alc Koh To Ii Roh Overset Pcl 5 To Overset Ag 2 O H 2 O To Configruation About Chiral Centre Is




Q5 Select The By Product Formed In The Reaction Roh Pclg Here A Is Rci A A Pocl2 Hci B H3po3 No Other By Product C H3po3 Hci




Iit Jee Chemical Reaction Of Alcohol With Hx Px3 Pcl5 Socl2 Nh3 In Hindi Offered By Unacademy




Reaction Of Alcohols With Pcl3 And Pbr3 Class 12 Youtube




Figure 5 1 Biocatalysis Applications Detergents Food Fibres Ppt Download




Sn1 Reaction Of Pcl5 With Roh Rcooh




Explain The Structure Of Pcl3 And Pcl5 Chemistry Topperlearning Com C9yvmoxx




Reaction Of Carboxylic Acids With Pcl5 Andpcl3 And Socl2 Youtube




What Is The Mechanism Of Reaction Between Alcohol And Pcl5 Chemistry Stack Exchange




Alcohols Nomenclature And Reactions Ppt Download




Group Differences On Pcl 5 Scores Download Table



What Will Be The Product When Pcl5 Reacts With Ethyl Alcohol Socratic



Alcohols Chemistry A Level Revision



1




Advanced Organic Synthesis Novasep



What Is The Mechanism For A Reaction Between Alcohol And Phosphorus Pentachloride Quora




05 Carboxylic Acid Reactions Of Carboxylic Acid With Pcl5 Pcl3 Socl2 Roh P2o5 Nh3 Dry Distilation Youtube



Among The Following The Number Of Compounds Than Can React With Pcl5 To Give Pocl3 Iso2 Co2 So2 H2o H2so4 P4o10correct Answer Is 5 Can You Explain This Answer Edurev Jee




Can Someone Please Help Me With These Diol Reaction Equations R Chemhelp



Org Chem Text Chapter 12 12 8 Htm




Ppt As Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Conversion Of Alcohols To Halide



Pbr3 And Socl2 Master Organic Chemistry




Catalysis Concepts And Green Applications Ppt Video Online Download
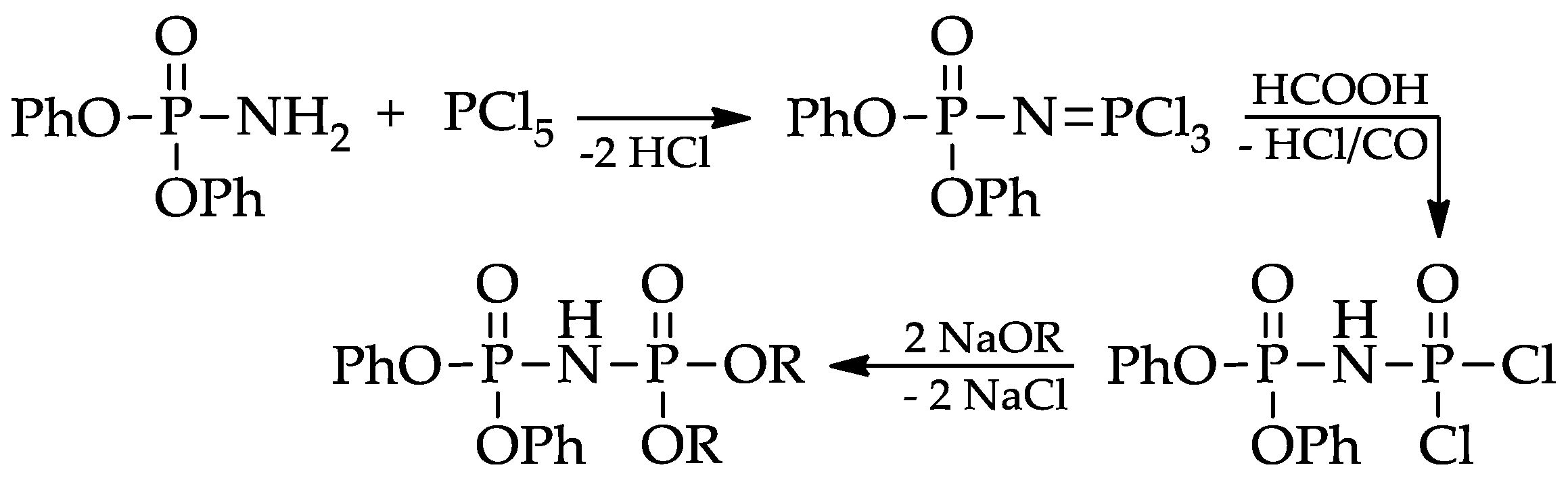



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Linear 2 Ethylhexyl Imidophosphoric Esters As Effective Rare Earth Element Extractants Html



What Happens When 1 Propanol Reacts With Pcl5 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Classification Of Alcohols Phenols And Cent Nbsp Classification Of Alcohols 1 Classification Of Alcohols Pdf Document



Mlsu Ac In




R Oh Pcl5 Gives To Brainly In




Bhartiyambhartiya Bhartiya With Your Class Section Rollno And Name Pcl5 H2o Acirc Dagger Rsquo H3po4 Hcl V Ba3n2 H2o Acirc Dagger Rsquo Ba Oh 2 Nh3 2 Pdf Document




Revisitation Of The Pcl5 Chlorination Reaction Of A Amino Acids Spectroscopic And Dft Insights And Synthesis Of The L Proline Derived 2 5 Diketopiperazine Sciencedirect




Group Differences On Pcl 5 Scores Download Table




0 1 Mol Of A Hydroxyl Compound Reacts With 62 5 G Of Pcl5 Mol Wt 8 5 Chemistry Alcohols Phenols And Ethers Meritnation Com




Aldehydes And Ketones Both Aldehydes And Ketones Contain Carbonyl Group C O The Difference Between Aldehyde And Ketone Was Found To Be In Aldehyde Ppt Video Online Download
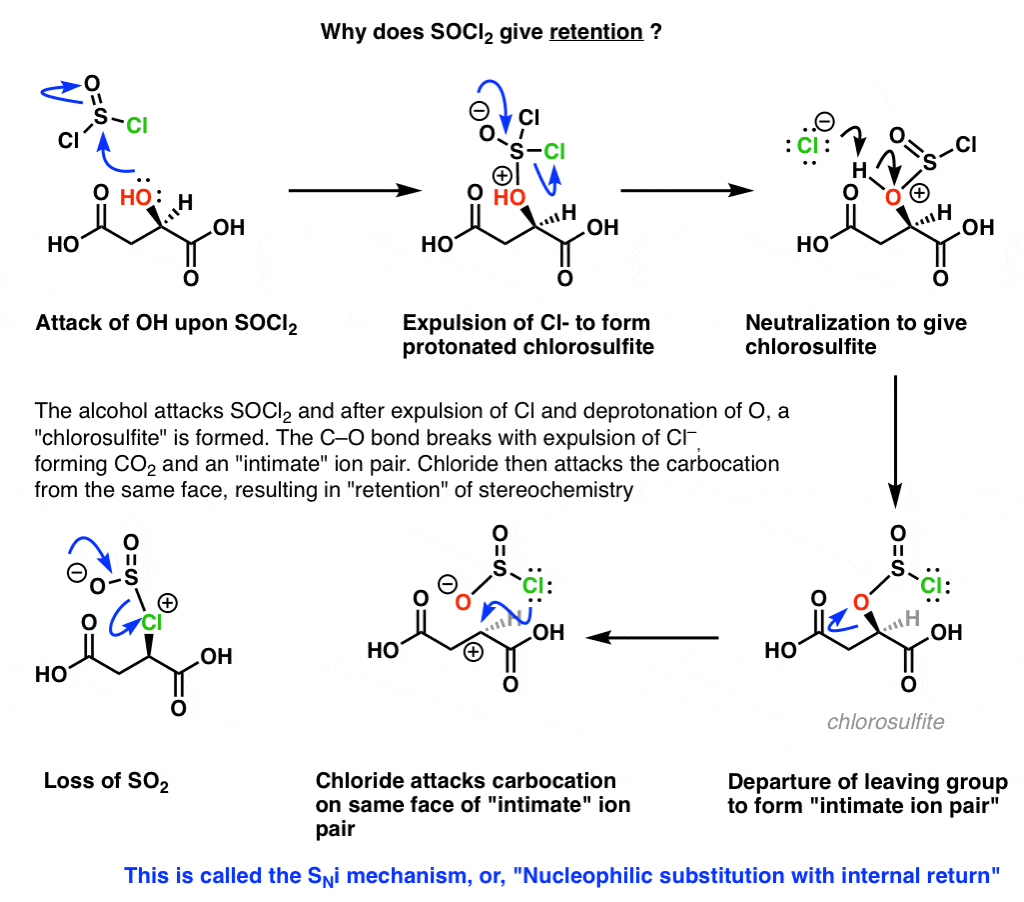



Socl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides Sn2 Versus Sni
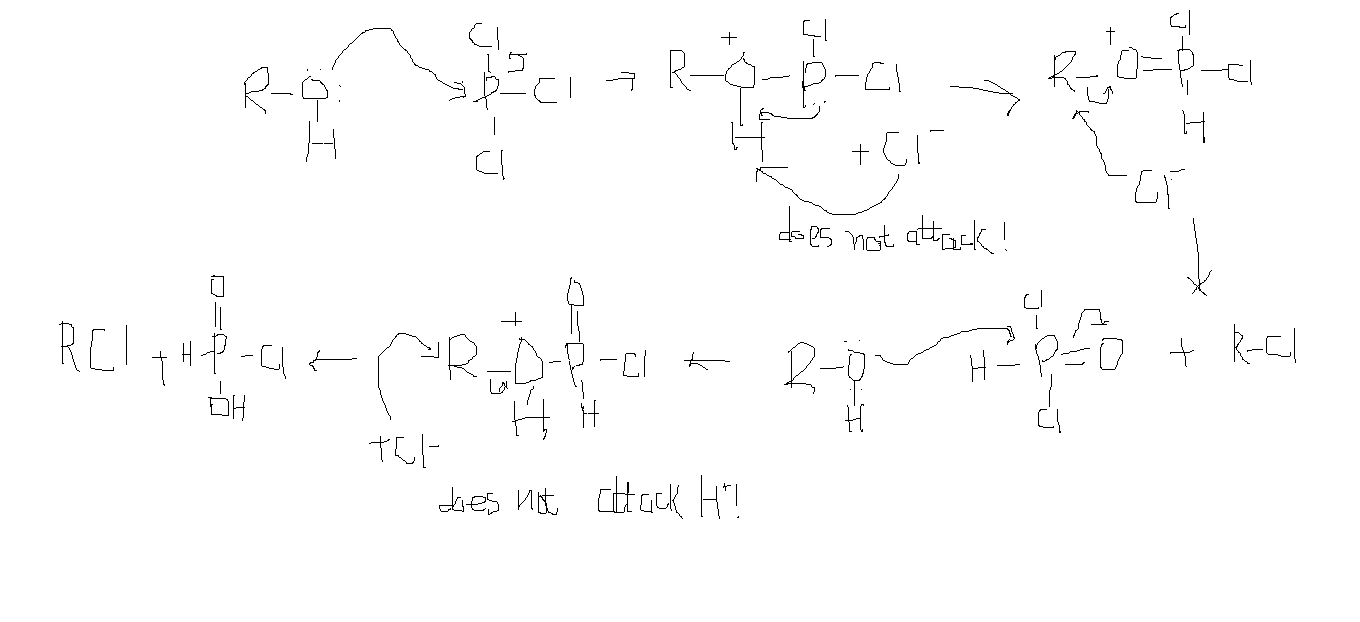



Mechanism For Roh Pcl5




Phosphorus Pentachloride Wikipedia




Alcohols And Ethers Alcohols R Oh Ethers Oh Hydroxyl Group Ppt Download




Preparation Of Alkyl Halides From Alcohols Video Khan Academy




Write The Chemical Reactions Of C2h5oh With Pcl3 And Pcl5 Separately



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿